
No one likes paying taxes. And that goes doubly for bootstrapping entrepreneurs trying to build income without the safety net of a W2 job.
But Uncle Sam sees it differently. The IRS expects self-employed people to pay double FICA taxes, covering both the employee’s side and the employer’s side of Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Which raises questions around whether real estate investors count as self-employed, in the eyes of Uncle Sam.
Do Landlords Owe Self-Employment Taxes?
In most cases, landlords don’t pay self-employment taxes on passive income from rental properties.
Emphasis on “passive income.” Your investment activity must be classified as passive, to avoid the IRS labeling it “earned income.” While rental income doesn’t always feel passive, you can usually claim it as passive as long as your entire livelihood doesn’t revolve around buying, renovating, and managing rental properties.
Even those who follow the BRRRR method can usually make a case for rental income being passive. But work with a clever accountant nonetheless.
You’ll track your rental income and expenses on Schedule D on your tax return. Your rental income, equal to your gross rental revenue minus all rental property deductions, is reported on your main form 1040 and is taxed at usual rates.
The self-employment tax norm for landlords does have a few exceptions. If you’re a real estate broker, for example, the IRS considers rental income as “earned income” and subjects it to self-employment tax.
Real estate owners must also record rent as self-employment income if they provide services to the inhabitants. That could include offering add-on services like dry cleaning or laundry services, or dog walking services.
What About Vacation Rental Owners?
If you own and manage Airbnb properties, you still don’t usually owe self-employment taxes if you just do it on the side of your full-time work.
But if you buy and manage vacation rentals for a living, speak with an accountant about how to keep classifying your income as passive, not earned.
Do House Flippers Owe Self-Employment Tax?
Where it gets blurrier is if you make a business of purchasing and selling real estate for a profit.
If you do one or two house flips a year, on the side of your full-time job, you can make a case that they represent investments and you only owe short-term capital gains tax, not self-employment taxes. But if your full-time gig is flipping houses, and you do ten a year? The IRS classifies you as a real estate dealer: someone in business and therefore owing self-employment taxes.
Report your rental income on Schedule C rather than Schedule E if it is deemed earned income. Both self-employment and regular income tax will apply to your net income from business activities, which is your total business revenues minus expenses.
While the IRS considers each case individually, if real estate investments account for more than half of your entire income, the IRS may consider your earnings to be earned income rather than passive income.
Independent contractors, such as real estate agents and property managers, must also pay both the employee’s and the employer’s parts of self-employment tax on their earnings.
How Is Real Estate Crowdfunding Income Taxed?
In most cases, real estate crowdfunding platforms send you a 1099-DIV at the end of each year, reporting your earnings as dividends.
The IRS taxes dividends at your regular income tax level. However you don’t pay self-employment taxes on them.
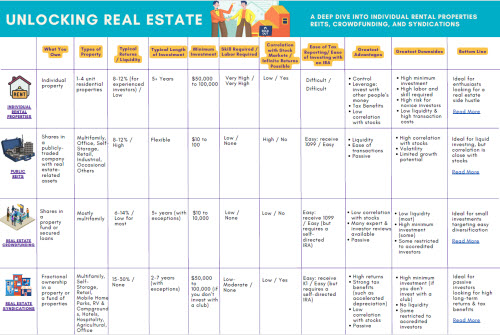
If you own fractional shares in a rental property, such as through Arrived Homes or SparkRental’s co-investing program, you pay capital gains taxes when the property sells, in addition to paying taxes on the rental income each year while you own it. See our full Arrived Homes review for more information about how their platform works.
Tips to Save Money on Taxes as a Real Estate Investor
Explore the following ideas to save money on your tax bill as a real estate investor.
Create an S-Corp
Rather than a sole proprietor or partner LLC, speak with a tax attorney or accountant about structuring your business as an S-corporation if you’re subject to self-employment taxes.
That can help you reduce self-employment taxes in a few ways:
- You avoid entity-level tax.
- The corporation pays you a small salary subject to self-employment tax, but sets aside the bulk of your income as distributions.
- Your distributive share of S corporation income is not subject to employment tax.
Other types of income are exempt from the employment tax and may be “manipulated” by some taxpayers in the same way that some S businesses pay wages.
But be careful in reclassifying your income as distributions rather than salary. The IRS wants S businesses to pay their shareholder-employees a reasonable compensation for services given to the company to avoid taxable revenue from being “converted” into investment income that is not subject to employment tax.
Talk to a CPA to determine the optimum tax deduction approach for you.
Hold Properties for at Least 1 Year
Flipping houses in a few weeks looks spectacular on TV, but if you sell a property in under a year, a significant amount of the profit will go to the IRS.
Any profit from an investment is classified as capital gains and is taxed based on your income and the length of time you’ve owned the property. Own an asset for less than a year, you’ll be subject to the income tax rate, which can be as high as 35%.
Hold an asset for at least a year and you pay the lower long-term capital gains tax rate.
Read up on other ideas to reduce or avoid capital gains taxes on real estate.
Do 1031 Exchanges to Keep Trading Up Properties
A like-kind exchange is a fantastic alternative to purchase a new property while avoiding capital gains taxes.
The provision, also known as a section 1031 exchange, permits you to “swap” one property for another of comparable value while deferring the tax bill.
Both the property you give up and the one you get must be used for investment, trade, or business to qualify. It must also be “like-kind,” both income-producing properties.
While a city block of land can be exchanged for a dairy farm in the country, the same city parcel cannot be exchanged for, say, a flat-bed truck.
Any real estate exchange for another piece of real estate, regardless of value.
(article continues below)
Keep Perfect Records of Expenses
Remember that self-employment tax is calculated on your net earnings, which is the amount left over after all expenses have been deducted.
As a result, make sure to keep detailed records of all your expenses to avoid paying more taxes than required
Always Depreciate Properties
The IRS lets you depreciate investment properties each year that you own them, for the first 27.5 years. Use our rental property depreciation calculator to run the numbers on how much you can deduct each year.
And remember, you’ll pay depreciation recapture tax when you sell the property whether you actually take depreciation or not. So if you don’t take it, you’ll pay taxes twice!
Pay Quarterly If You Owe Self-Employment Taxes
If you have to make quarterly estimated tax payments, make sure you do so on schedule to avoid penalties.
Set away at least one-third of all your earnings in a separate savings account after accounting for self-employment tax.
Final Thoughts
If you’re a rental property investor, you’re probably planning on keeping your property for more than a year, which means your real estate taxes will be lower in the long run, giving you the advantage.
A knowledgeable tax professional can assist you in determining your self-employment tax due and ensuring timely payment of your taxes. When tax season comes around, you won’t be caught off guard if you’ve done your homework and followed the recommendations.♦
How do you reduce your taxes as a real estate investor? Do you pay any self-employment taxes?
More Real Estate Investing Reads:
About the Author

Camron Hoorfar is a licensed attorney with experience in consumer debt, litigation, bankruptcy, tax, business laws, criminal laws, and non-profit organizations. He is also the spokesperson of Debt Consolidation Care — the Internet’s get out of debt community.
























These are great tips. Appreciate your sharing it!
Thanks Sam!
Same question in mind! Thank you for answering.
Glad to hear it was helpful Jeremy!
Taxes taxes. Who likes paying taxes. I wish there was no such thing as a tax!
Haha, I hear you Mike!
Airbnb can help you avoid taxes, if that’s the case we should only do Airbnb then, Lol.
How does Airbnb help you avoid taxes?
These are excellent tips on reducing taxes. Thank you for sharing!
I almost overlooked my taxes for my Airbnb apartments. Good thing I hired an accountant to help out.
Always gotta be careful with the IRS Vincent!